
Skin Conditions Explained

Eczema
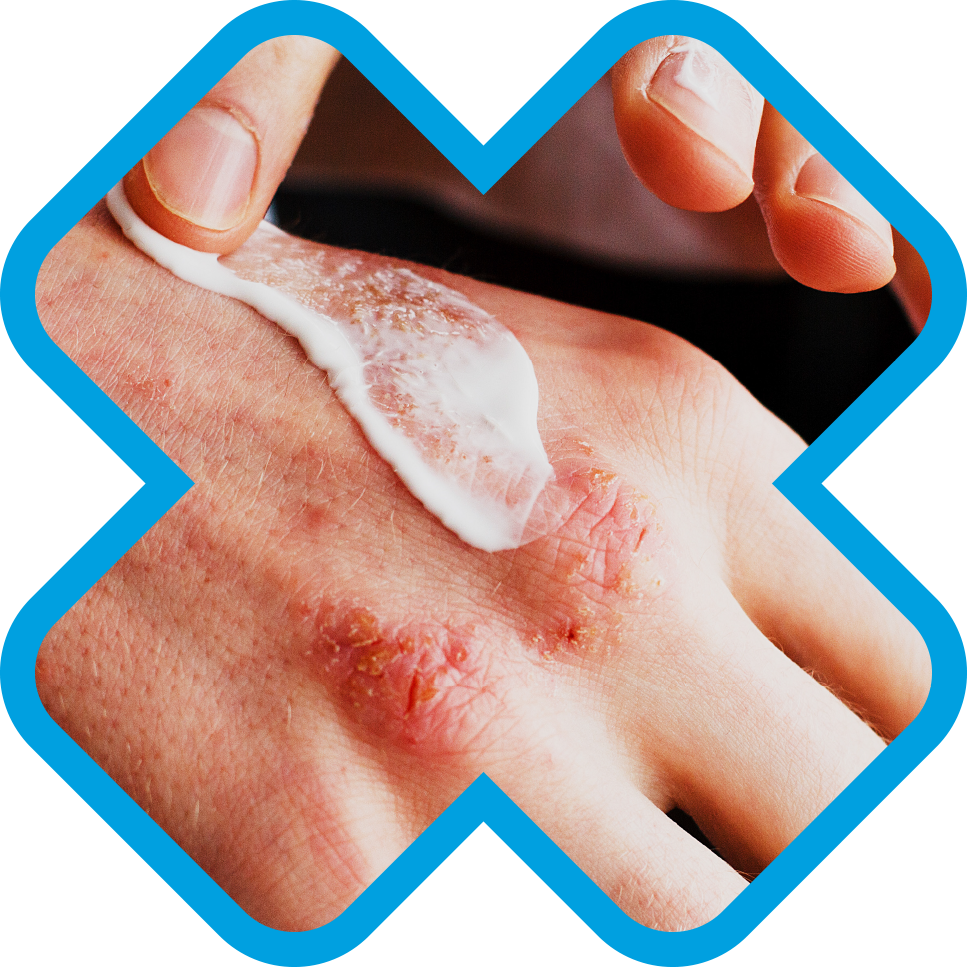
Eczema (or dermatitis) can affect anyone. It is a non-contagious skin condition that sees the skin become irritated and itchy, often being red and sometimes swollen and blistered. Eczema can vary in severity from person to person with different types having different causes and treatments.
There are many types of Eczema that can affect different parts of the body, the most common being hand eczema. Eczema can come and go or it may be long standing. Atopic Eczema sufferers may also have asthma or hay fever, often starting before the age of one.
General symptoms of Eczema include:
Dry, cracked skin that has become sore and red
Extreme itchiness (which when scratched may bleed)
Sometimes blisters will develop
Any part of the body, including the hands and face, can be affected
Causes of Eczema
Eczema commonly arises when the skin comes into contact with either a particular substance to which it has an allergic reaction to, an irritant or simply due to essential moisture being lost as a result of excessive washing.
Common allergens and irritants include:
Fragrances usually used in soaps and shower gels
Rubber
Construction products such as cement
Preservative chemicals
Cleaning agents and detergents
Dust
Excessive hand washing
Swimming
Stress can also be a cause of eczema or irritate the condition further.
Psoriasis
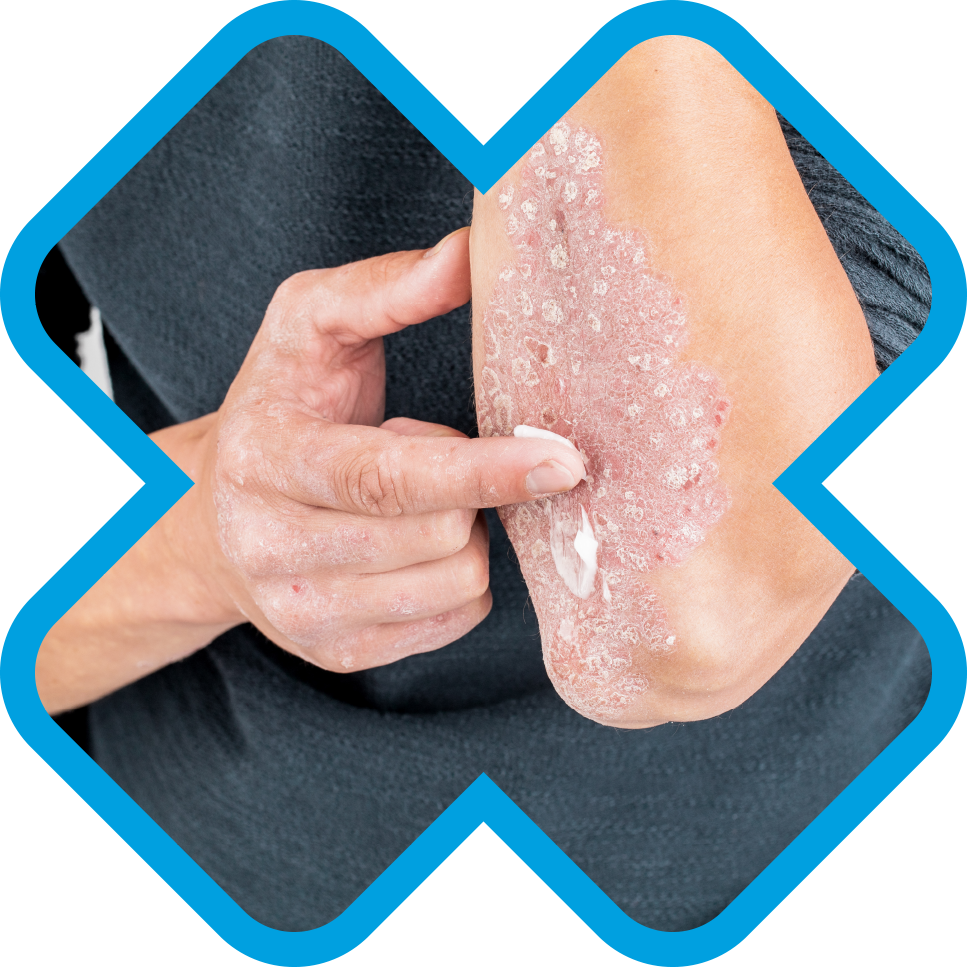
Psoriasis is a non-contagious autoimmune condition (a condition that occurs when the body tissues are attacked by its own immune system). Psoriasis causes skin cells to develop rapidly building up on the skin resulting in thick, scaly, crusty patches.
It is important that a doctor or a health care professional diagnoses your Psoriasis.
General symptoms of Psoriasis:
Red, flaky sometimes crusty patches of skin
Patches can appear anywhere on the body but would normally tend to appear on the elbows, knees, scalp and lower back
Causes of Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is a non-contagious skin condition, thought to be related to the sufferer’s immune system
It can often run in families
It sees the natural skin cell replacement process taking between 3-7 days, as opposed to the normal rate of 3-4 weeks
Symptoms often start or worsen because of a trigger, e.g. certain medications, infections or skin injuries
Ichthyosis
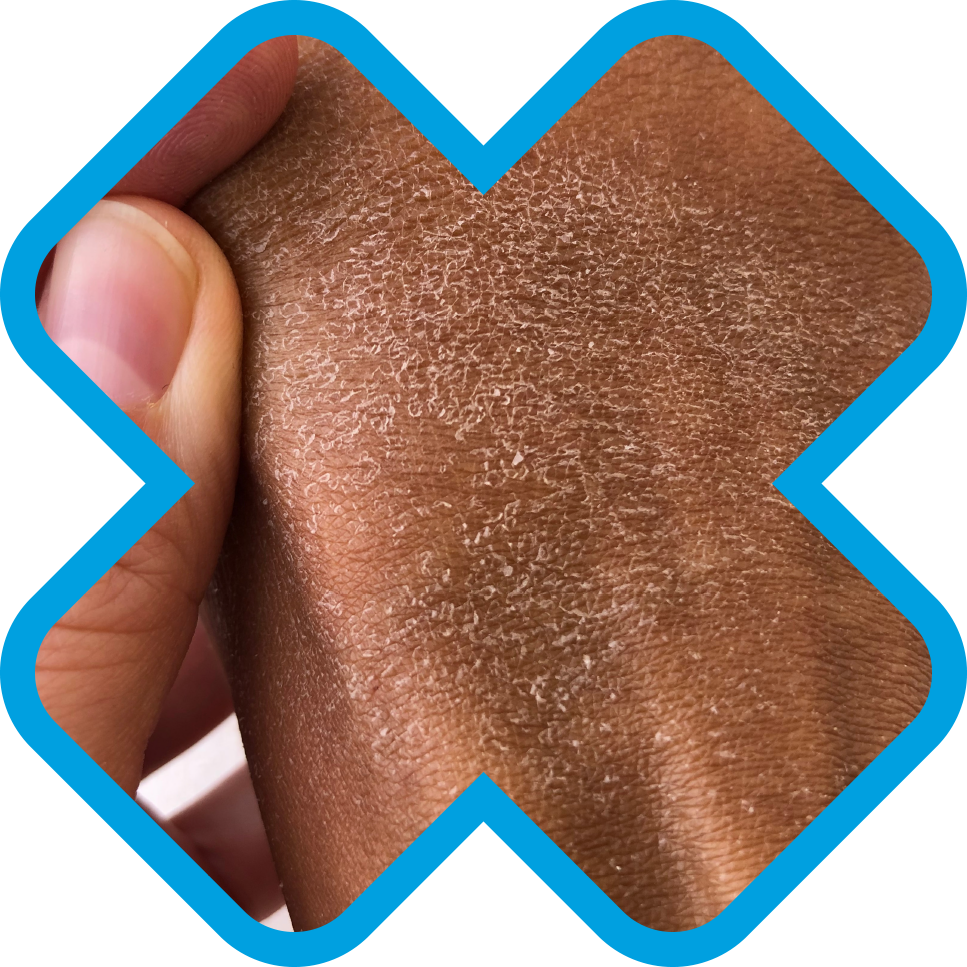
As with Psoriasis, Ichthyosis is also non-contagious skin condition, however unlike both Eczema and Psoriasis, Ichthyosis is genetic skin disorder and so a family history of the condition may increase the likelihood of you developing it.
It is important that a doctor or a health care professional diagnoses your Ichthyosis.
Characterised with dry, scaly and thickening skin, common symptoms of Ichthyosis include:
Scales that are formed on the skin – this will main occur on the torso and legs
Itchiness
Patches of redness on the skin usually as a result of injury or irritation – this is commonly known as Erythema
Peeling or painfully cracked skin
Causes of Ichthyosis:
Ichthyosis is a genetic skin condition and will not be caused by irritants
It is important that you use the above as general information only. It is essential that you consult with your doctor or a health care professional for any medical advice or information about diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions.
X-tra Info
For more independent information about skin conditions and the safe use of emollient products click on the relevant link below:
Skin conditions
Emollient products
Which emollient product is right for you and how and when to use it – here
Safe use of emollients
It is essential that when using any emollient gel, cream, ointment or barrier cream you take care to ensure they do not dry onto clothing, bedding or dressings as this can make them flammable – here
